OLSAT Test: Full Guide
This article includes affiliate links. If you use these links to buy something we may earn a commission. Every service or product is selected independently by Aptitudetest24.com.
A multiple-choice test known as the Otis-Lennon School Ability Test (OLSAT), produced by Pearson NNC, is frequently used in the US to identify gifted children. Schools frequently use the OLSAT to assess student achievement across all age groups or as a tool for admittance into schools and programs for gifted and talented children.
The verbal and nonverbal components of the OLSAT test a student's aptitude for handling academic assignments. The OLSAT has 21 different question categories in total. Students must follow instructions, recognize similarities and differences, remember words and numbers, classify items, build sequences, solve arithmetic problems, and complete analogies on the exam.
The OLSAT is developed primarily to assess cognitive and logical abilities important for academic success. The OLSAT is designed to evaluate one's memory, mental agility, and capacity for linkages and patterns. Instead of other, more specialized, and mechanical domains, the verbal-academic domain was the focus of the OLSAT's design.
Test levels in OLSAT
OLSAT Level A, OLSAT Level B, OLSAT Level C, OLSAT Level D, OLSAT Level E, OLSAT Level F, and OLSAT Level G are the seven levels at which the OLSAT test is given, depending on the age of the student. Level A represents pre-kindergarten and Olsat kindergarten. The Otis-Lennon School Ability Test has four test levels, with level A being the lowest. At this level, basic information that isn't generally covered in school is evaluated together with a child's ability to follow instructions.
Level B represents Grade 1. The OLSAT Level B test is designed to identify kids who should be admitted to a gifted and talented program by giving parents and teachers crucial information about the kids' learning capacities and talents.
Level C represents Grade 2. Children in second grade take the OLSAT level C, a multiple-choice test designed to assess reasoning, verbal, and nonverbal skills. The test is frequently given to kids to assess their academic development and identify their strengths and weaknesses.
Olsat practice test level D represents Grade 3. Unlike most tests, this one assesses a child's verbal and nonverbal cognitive abilities and does not directly measure what they have learned in school. Instead, this exam aims to gauge students' capacity for knowledge comprehension and inference.
Olsat level E represents Grades 4 to 5. The test measures a child's verbal and nonverbal skills using multiple choice questions.
Olsat level F represents Grades 6 to 8. Level F targets grade appropriate quantitative and qualitative content areas, and like the other OLSAT levels, becomes progressively more difficult.
Olsat level G represents 9 to 12.
Depending on the OLSAT test level, the student will have 60 to 80 minutes to complete a 40 to 70-question test. Younger students take a test such as the Olsat test kindergarten in a one-on-one environment, whilst older children like Olsat level e practice test do in a group setting.
The order of exam questions prevents questions from getting harder as the test goes on. To avoid students becoming disheartened when faced with increasingly challenging questions, simple questions are occasionally followed.
The OLSAT Test online is notoriously challenging, and students must obtain high OLSAT exam scores to be accepted into prestigious programs or special schools for gifted and talented children.
OLSAT sample question types
Free OLSAT practice test for the non-verbal section
OLSAT Pictorial Reasoning
Picture Classification, Picture Analogies, and Picture Series are the three question types included in the Pictorial Reasoning category. These inquiries test a child's capacity to make connections between various images and illustrations, identify similarities and contrasts between objects, and comprehend and carry out progressions. Questions about picture classification test your capacity to spot the strange one. Questions involving picture analogies measure a person's comprehension of the connections between images. Picture Analogy items evaluate the capacity to recognize similarities whereas Picture Classification items evaluate the capacity to recognize distinctions. The understanding of progressions and patterns is tested through Picture Series questions.
OLSAT Figural Reasoning
Four different types of questions fall under the Olsat 8 practice test figural reasoning category: Figural Classification, Figural Analogies, Pattern Matrix, and Figural Series. These inquiries test a child's capacity to apply geometric figures and forms to deduce associations, comprehend and carry out progressions, and contrast and compare various figures. Figural Classification tests a candidate's aptitude for spotting the odd one out. Figural Analogies test your understanding of how figures relate to one another. Figural Analogy evaluates the capacity to recognize similarities, while Figural Classification evaluates the capacity to recognize distinctions. Pattern Matrix tests gauge how well you can complete a matrix by adding the missing piece. Figural Series questions test a student's aptitude for anticipating the next geometric shape in a series.
OLSAT Quantitative Reasoning
Number Series, Numeric Inference, and Number Matrix are the three main sorts of questions that can be found in the Quantitative Reasoning area of the Olsat sample test. These inquiries test a student's capacity to deduce and apply computational rules in a given situation and infer relationships between numbers. Number Series questions test a candidate's capacity to recognize a pattern in a list of numbers or characters as well as their capacity to complete a series that is missing an item. Numerical inference problems test the understanding of connections between numbers and number groups. The capacity to complete the blanks in a matrix consisting solely of numbers is tested by number matrix problems.
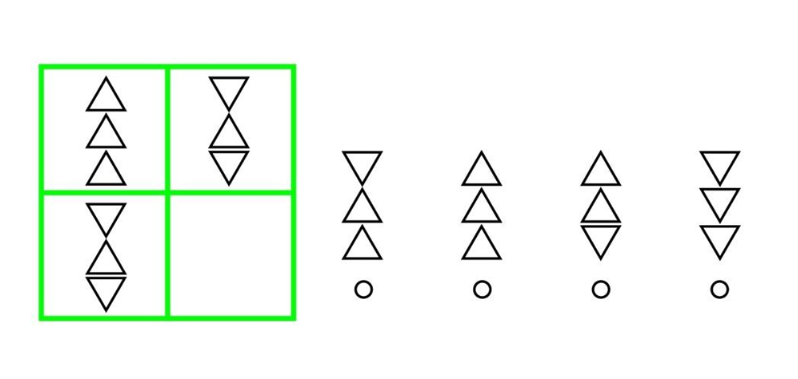
Free OLSAT practice test for the non-verbal section
Look at the shapes diagonally in the top two boxes. They go together in a certain way. Look at the shapes on the side. Which of the shapes tally?
Option A
Option B
Option C
Option D
B is the answer because it tallies with the shape inside the box diagonal to it.
How to score OLSAT test in 2025
Students do not lose points for skipping or providing a false answer; instead, they gain points for each question they correctly respond to. A child receives a raw score, indicating how many of the test's total questions were successfully answered when graded.
The result is transformed into a School Ability Index (SAI) score after the calculation of the raw score. The SAI score is calculated by contrasting the raw scores of other kids in the same age group. It has a maximum score of 150, a standard deviation of 16, and a normalized average of 100.
The student's percentile is then determined using this SAI score. Students who achieve a score of 132, or two standard deviations above the mean, typically fall between the 97th and 98th percentile, or the top 2-3% of students.
OLSAT test prep for verbal comprehension section
Four types of questions fall under the Verbal Comprehension category: Following Directions, Antonyms, Sentence Completion, and Sentence Arrangement. These inquiries test a child's capacity to recognize and comprehend word relationships, recognize various word meanings depending on the context, and be able to combine words and phrases meaningfully.
Children's listening and understanding skills as well as their ability to match descriptions to pictures, are tested by following directions questions, which are read aloud by the proctor. Questions about antonyms evaluate a child's vocabulary by asking them to grasp and recognize words with different meanings. While understanding antonyms is thought to be more challenging, identifying antonyms is similar to identifying synonyms.
Sentence completion tests measure a person's capacity to finish a sentence in a logical manner. The ability to correctly choose the words or phrases that the sentence needs in order to make sense is tested through sentence completion exercises. Questions about sentence structure evaluate your capacity to comprehend how the relationships between words in a sentence contribute to its meaning. Questions about sentence structure test your ability to combine a group of words to form a whole sentence.
Importance of OLSAT test prep
The OLSAT 8 is a common tool used in the educational system to assess children's levels of giftedness for a number of reasons. First off, the OLSAT is known for being a trustworthy exam. According to studies, a child's OLSAT score won't dramatically vary over time. Second, studies show that the OLSAT successfully evaluates the components of intelligence it wants to measure, which is why it is regarded as a valid exam. In terms of testing many kids, the OLSAT 8 is a convenient, affordable option for schools. The OLSAT 8 has also been peer edited by a group of educators from minority groups to assist reduce biases related to race, gender, culture, or geography.
How to scale through the OLSAT sample test
The OLSAT 8 is a challenging exam, so it's crucial for your child to be ready on test day, especially with the level of competition for gifted programs at an all-time high. Here, there are grade-specific practice packs for kids with helpful study materials, practice exams based on real exams, and hundreds of additional practice questions. Start by taking our free OLSAT practice test or go through the Olsat practice questions.
Conclusion
Parents can aid children, and instructors can safely adapt instruction to students using OLSAT tests as a component of a thorough and balanced assessment strategy. Realistic learning objectives for each subject area are in OLSAT reports so that parents may see their kids’ progress and be motivated to take control of their learning.